Calculating income tax is an essential aspect of managing your personal or business finances. Understanding the process of income tax calculation can help you plan your financial affairs more efficiently and ensure compliance with the tax regulations in your country. In this article, we will provide you with a step-by-step guide on how to calculate income tax.
Table of Contents
Step 1: Determine Your Taxable Income:
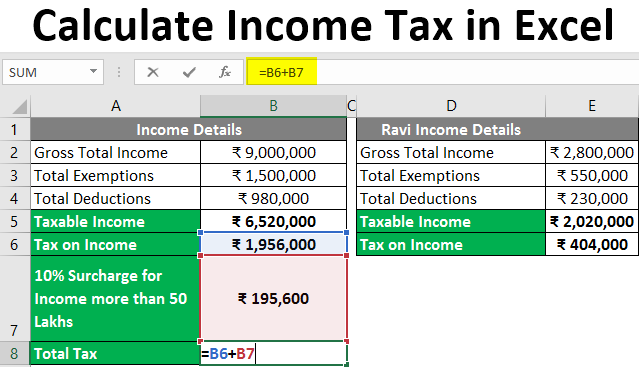
Taxable income refers to the amount of income you earn that is subject to taxation after deducting eligible expenses and allowances. Start by identifying all your sources of income, including salary, wages, rental income, dividends, interest, and any other taxable earnings. Subtract any applicable deductions, such as business expenses, contributions to retirement accounts, or student loan interest payments. The resulting figure is your taxable income.
Step 2: Understand The Tax Brackets:
Most countries have a progressive tax system where tax rates increase as income rises. Tax brackets define different income ranges, each with its corresponding tax rate. Obtain the latest tax brackets and rates from your country’s tax authority or the official government website.
Step 3: Calculate Tax Liability:
To calculate your tax liability, apply the appropriate tax rate to each tax bracket your income falls into. For instance, if your taxable income falls within the first tax bracket, you will apply the tax rate associated with that bracket to the corresponding income range. Repeat this process for each tax bracket until you have accounted for your entire taxable income. Add up the resulting tax amounts from each bracket to obtain your total tax liability.
Step 4: Account For Deductions And Credits:
After calculating your initial tax liability, you may be eligible for deductions or tax credits that can reduce the overall amount of tax you owe. Deductions, such as mortgage interest, charitable contributions, or education expenses, directly reduce your taxable income. Tax credits, on the other hand, are subtracted from the tax liability itself, providing a dollar-for-dollar reduction. Ensure that you are aware of the available deductions and credits in your country and apply them accurately to arrive at your final tax liability.
Step 5: Consider Additional Taxes:
In addition to income tax, certain jurisdictions impose other taxes such as social security contributions, self-employment taxes, or local taxes. Make sure to account for these additional taxes if they apply to your situation. Check the relevant laws and regulations or consult with a tax professional to ensure accurate calculation and compliance. You can also get help from tax tools like tax calculators. This powerful tool takes into account the latest tax laws and regulations, ensuring that users receive accurate results tailored to their specific circumstances.
Step 6: Complete And File Your Tax Return:
Once you have calculated your final tax liability, it’s time to complete your tax return. Use the appropriate tax forms provided by your tax authority and accurately report your income, deductions, and tax credits. Ensure all necessary supporting documentation is attached. File your tax return by the specified deadline, whether electronically or by mail, to avoid penalties or late fees.
Step 7: Utilize Tax Calculation Tools Or Software:
To simplify the income tax calculation process, you can leverage various tax calculation tools or software available online. These tools often incorporate the latest tax rates and brackets, automatically perform the necessary calculations, and help ensure accuracy. They can save you time and effort, especially when dealing with complex tax scenarios or multiple sources of income.
Step 8: Be Aware Of Tax Deductions And Exemptions:
In addition to the deductions and credits mentioned earlier, it is essential to be knowledgeable about specific tax deductions and exemptions that may apply to your situation. These could include deductions for medical expenses, home office expenses, or contributions to retirement accounts. Similarly, exemptions may be available for dependents or specific income categories. Stay informed about these options to maximize your tax savings.
Step 9: Consider The Impact Of Tax Planning:
Tax planning involves strategic decisions and actions taken throughout the year to optimize your tax position. By understanding the tax rules and regulations, you can make informed choices that minimize your tax liability. For example, you might decide to defer income or accelerate deductions to lower your taxable income in a particular year. Tax planning can be complex, so consult with a tax professional or financial advisor to develop an effective tax strategy.
Conclusion:
Calculating income tax requires careful consideration of taxable income, tax brackets, deductions, and credits. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can navigate the process with confidence. Remember, tax laws may change over time, so stay updated with the latest regulations or seek professional advice when needed. Properly calculating and paying income tax is not only a legal obligation but also an essential part of maintaining your financial well-being.
Also Read: calculate-age-from-date-of-birth
Be First to Comment